One of the barriers preventing the universal acceptance of foam sclerotherapy for superficial tributaries is the real side-effect of post inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) and pain at the site of the sclero-thrombosis. Although a sclerosis is the optimal process to achieve a good result, adequate collapse of the target vein is rarely achieved using eccentric compression with pads, pledgets or dental swabs, unless very high compression pressures are used. The principal of tangential compression with kinesiotape is discussed.
PATRICIA CRISTODOR We have been using kinesiotape for many years as a solution for a large variety of problems. These include the relief of tension across surgical wounds and the reduction of biomechanical stress over joints. This leads to a reduction in scar tissue formation, facilitates wound healing and allows joints to recover from injury or other inflammatory conditions.
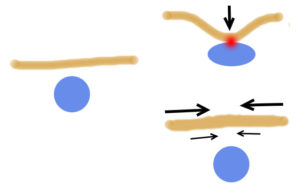
A recent innovation is the use of kinesiotape for the treatment of varicose veins. The optimal environment for treating a vein with foam sclerotherapy is to ensure complete collapse of the vein so that the foam reacts with the endothelium and penetrates into the deeper tissues. However, this is difficult to achieve because most veins are just pushed towards the skin with eccentric compression or ovalise without a significant reduction in cross-sectional area. Furthermore, eccentric compression approximates the skin to the inflamed vein and this may result in the side-effects of PIH and pain.
Tangential compression with kinesiotape separates the skin from the vein. It is applied during tension across 50% of the circumference of the leg. On adherence, the tape retracts to its normal length. Its use in ultrasound guided foam sclerotherapy (UGFS) has yet to be proven.
The effect of eccentric compression (upper right) and tangential compression with kinesiotape (lower right) on the target vein (left). Note that eccentric compression approximates the skin to the vein with an insignificant effect on cross-sectional area.
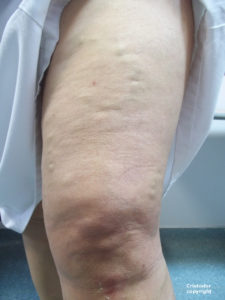
A leg with mild superficial varicose veins before the application of kinesiotape.
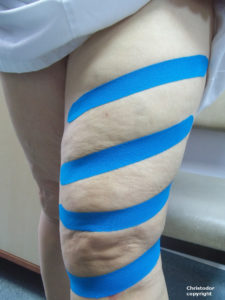
Widely separated kinesiotape to illustrate its effects on submerging the varicosities.